 忧郁的大能猫
忧郁的大能猫
好奇的探索者,理性的思考者,踏实的行动者。
blog/A-IT/10-编程语言/c.c++/c笔记/c零碎知识点
Table of Contents:
__typeof__()并且__typeof()是C语言的编译器专用扩展,因为标准C不包含这样的运算符。标准C要求编译器用双下划线前缀语言扩展(这也是为什么你不应该为自己的函数,变量等做这些)
C++ 程序员偏向于使用 for(;;) 结构来表示一个无限循环。
vs中查看string的中文字
在获取包含中文变量的时候,查看std::string字符串变量,提示:字符串中的字符无效
变量后加,s8 即可
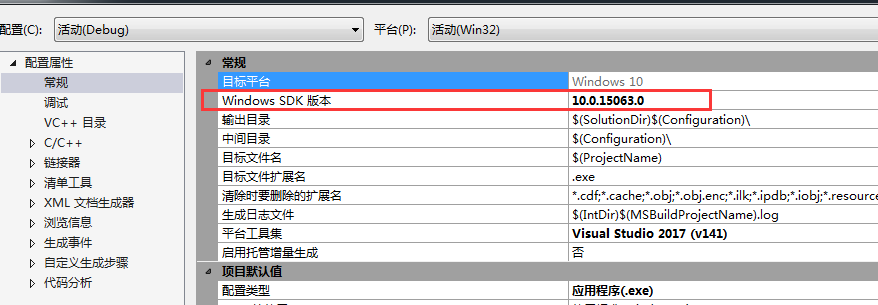
vs设置Windows SDK
#include <WinSock2.h>vs中显示winsock2.h 找不到,于是搜索了下发现在
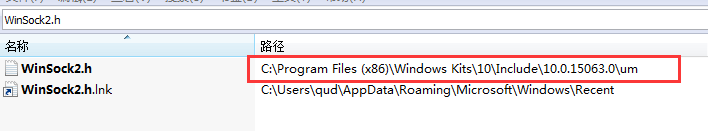
于是更改了下Windows sdk就好了
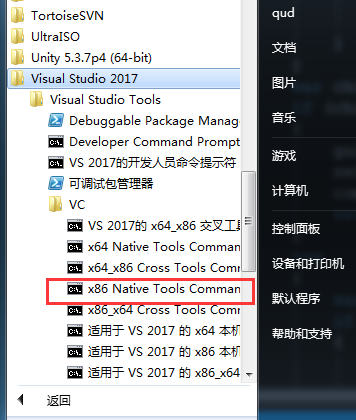
VS命令行编译
在tools下有个bat文件VsDevCmd.bat,运行后就可以把编译的命令设置到环境变量中,然后就可以在命令行中编译了
.net framework ^符号
在MSDN看到这个“^”符号,它究竟是什么意思?不是位运算符哈。
public static DirectoryInfo^ CreateDirectory(
String^ path
)这个是c++调用.net framework库里面的对象用到的符号,DirectoryInfo和String都是.net对象,你把^当作一种特殊的指针看就可以了。
linux man
man fopen 在linux下就可以查看到c函数的用法
c函数(尤其linux下)正确情况一般返回 0 ,错误的话则返回错误码
DLL _declspec
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<windows.h>
// _declspec(dllexport) 告诉外部可以调用,没有的话外部不可调用
_declspec(dllexport) void goA() 不需要main函数
{
while (1)
{
MessageBoxA(0, "你在与间谍聊天", "请注意安全", 0);
}
}
要编译成dll的文件,注入到其他程序中CGI
CGI:早期动态网页技术使用最多的,发展的比较成熟并且功能强大,但是效率比较低,编程比较困难。目前很少使用CGI做动态网页。CGI就是web服务器提供的一个可以执行服务器端程序接口的东西,可以用c c++ python 等各来写种语言
一个网站的后门cgi程序,可以执行各种系统的命令,当然用php也可以这样做的
void main()
{
printf("Content-type:text/html\n\n");
printf("%s<br><br>", getenv("QUERY_STRING")); //打印环境变量,由web服务器传入
char szPost[256] = {0};
gets(szPost);//获取输入
printf("%s<br><br>", szPost);//获取输入
//"BBB=tasklist&AAA=%C7%EB%BD%F8
char *p = szPost + 4;//0,1,2,3
char *p1 = strchr(szPost, '&');
*p1 = '\0'; //弄个结束的位置
char cmd[256] = { 0 };
sprintf(cmd, "%s >1.txt", p);//字符串映射
system(cmd);
FILE *pf = fopen("1.txt", "r");
while (!feof(pf))//如果没有到文件末尾就继续
{
char ch = fgetc(pf);
if (ch == '\n')
{
printf("<br><br>");//换行
}
else
{
putchar(ch);//打印字符
}
}
}外挂的思路
植物大战僵尸外挂的思路
知道那些地址代表那些属性,然后修改之,(属性包括游戏运行暂停状态,分数,生命值……)这就是外挂可以通过使用Cheat Engine 来扫描比如阳光的地址,然后修改地址,最重要的是扫描出基址,和各个属性的偏移地址。然后根据这些地址写一个修改地址的dll,然后注入到游戏中
示例代码
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
//1.在c中没有字符串这种类型,是通过字符串数组(char buf[100])去模拟
//2.字符串和字符串数组的区别 是不是 带有\0
//字符串数组 也是 数组
void main11()
{
//通过字符串常量初始化字符串数组
//通过这种方法它会自动给你\0
char buf4[] = "abcdefg";
printf("%s\n", buf4);
system("pause");
}
//strlen() 是一个函数 求字符串的长度,不包括\0
//sizeof() 是一个操作符,求数据类型(实体)的大小(单位:字节)
void main12()
{
char buf3[] = {'a', 'b', 'c', '\0'}; //buf是个指针
printf("strlen(buf3):%d \n", strlen(buf3)); //3
printf("sizeof(buf3)%d \n", sizeof(buf3));//4
system("pause");
}
int main()
{
char *p1 = "111111";
char *p2 = malloc(100); //sizeof(p2) = 4 32位 = 4 64位 = 8
strcpy(p2, "3333");
}
-------------统计str里有几个substr-------------
void main()
{
char *p = "abcd1111abcd222abcd3333";
int ncout = 0;
while (p = strstr(p, "abcd"))
{
p = p + strlen("abcd"); // 未找到则返回 NULL。
ncout ++;
if (*p == '\0')
{
break;
}
}
printf("ncout:%d\n", ncout);
system("pause");
}
//不要相信别人给你传送的内存地址是可用的
int getCout(char *str, char *substr, int *count)
{
int rv = 0;
char *p = str;
int ncout = 0;
if (str==NULL || substr== NULL || count==NULL)
{
rv = -1;
printf("func getCout()check (str==NULL || substr== NULL || count==NULL) err:%d \n" , rv);
return rv;
}
do
{
p = strstr(p, substr);
if (p == NULL) //没有找到则跳出来
{
break;
}
else
{
ncout++;
p = p + strlen(substr);
}
} while (*p != '\0');
*count = ncout;
return rv;
}
--------------字符串复制-------------------
//因为后缀++的优先级,高于,*p;
void copy_str3(char *from , char *to)
{
int ret = 0;
if (from ==NULL || to== NULL)
{
ret = -1;
printf("func copy_str2() err: %d, (from ==NULL || to== NULL)", ret);
return ret;
}
while(*from != '\0')
{
// *to = *from;
// to ++;
// from ++;
*to ++ = *from++;
}
*to = '\0';
return ret;
}
void copy_str4(char *from , char *to)
{
while((*to++ = *from++) != '\0')
{
;
}
}
----------------去两边的空格,两头堵-----------------
//char *p = " abcd11111abcd2222abcdqqqqq ";
void main41()
{
int count = 0; //去除空格后的长度
int i = 0, j = 0;
char *p = " abcd ";
j = strlen(p) -1;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && j>0)
{
j--;
}
count = j-i +1;
printf("count:%d", count);
system("pause");
}
//封装成函数
int trimSpace(char *mybuf)
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0, j = 0;
char *p = mybuf;
j = strlen(p) -1;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && j>0)
{
j--;
}
count = j-i +1;
printf("count:%d", count);
//void * __cdecl memcpy(void *, const void *, size_t);
memcpy(mybuf, mybuf+i, count);
mybuf[count] = '\0';
return 0;
}
//改进版
//一般情况下不要修改输入的内存块的值,一般有输入参数和输出参数
int trimSpace(char *mybuf, char *outbuf)
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0, j = 0;
char *p = mybuf; //付给一个值,以免这个指针找不到了,比如 ++操作后
j = strlen(p) -1;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && j>0)
{
j--;
}
count = j-i +1;
printf("count:%d", count);
//void * __cdecl memcpy(void *, const void *, size_t);
memcpy(outbuf, mybuf+i, count);
outbuf[count] = '\0';
return 0;
}
-------------字符串反转----------------
void main()
{
//char *str = "abcdefg"; 因为他是在全局区,没法改变的
char str[] = "abcdefg"; //在栈区的可以修改
int len = strlen(str);
char *p1 = str;
char *p2 = str + len -1;
while(p1 < p2)
{
char c = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = c;
p1 ++;
p2 --;
}
printf("str:%s\n", str);
system("pause");
}
----------------------配置文件查找------------------------------
int getKeyByValude(char *keyvaluebuf /*in*/, char *keybuf /*in*/,
char *valuebuf /*in out*/, int * valuebuflen /*in out*/)
{
// 检查参数合法性
int rv = 0;
char tmp[2048*10];
char *p = NULL;
//1. 在大字符串里面查找有么有关键字
p = strstr(keyvaluebuf, keybuf);
if (p==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
p = p + strlen(keybuf);
//2. 再查找=号
p = strstr(keyvaluebuf, "=");
if (p==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
p = p + 1;
//3 去掉左右空格
rv = trimSpace_ok2(p, tmp);
if (rv != 0)
{
printf("func trimSpace_ok2() err:%d\n", rv);
return rv;
}
strcpy(valuebuf, tmp);
*valuebuflen = strlen(tmp);
return 0;
}
void main()
{
int rv = 0;
char keyvaluebuf[] = "ORACLE_name = itcast ";
char *keybuf = "ORACLE_name";
char valuebuf[1024];
int valuebuflen = 0;
//调用函数,要先判断是否出错
rv = getKeyByValude(keyvaluebuf, keybuf, valuebuf, &valuebuflen);
if (rv != 0)
{
printf("func getKeyByValude() err:%d", rv);
return ;
}
printf("valuebuf:%s\n", valuebuf);
printf("valuebuflen:%d\n", valuebuflen);
system("pause");
}
void main02()
{
//我声明了一个数组类型
typedef int(MyArr5)[5]; //5个int类型的内存空间,也就是类型的长度
//用数据类型定义一个变量
MyArr5 arr5; //相当于int arra[5];
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
{
arr5[i] = i+1;
}
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
{
printf("%d \n", arr5[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", (int)sizeof(arr5)); //20
//指针步长是20
printf("%p %p\n", &arr5, &arr5 + 1); //0x7fffb9a9d500 0x7fffb9a9d514
system("pause");
}
--------------指向数组类型的指针变量----------
void main022()
{
int a;
int *p = NULL;
int i = 0;
//我声明了一个数组类型 (固定大小内存块的别名)
typedef int(MyArr5)[5];
//定义一个指向数组类型的指针变量
MyArr5 *pArray;// &a;
int a1[5] = {1,3,4,55, 6};
//给数组指针赋值 需要。。。&a1
MyArr5 *pArray = &a1; //4个字节
//用数组指针去遍历数组
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
{
printf("%d ", (*pArray)[i]);
}
system("pause");
}
//c库函数读写二进制文件的代码,linux下不区分文本文件和二进制文件,所以也就没有win下的b的读写模式
//二进制文件必须知道文件的格式才能解析出来
struct person
{
int id;
char name[20];
int age;
int sex;
char tel[20];
};
//读结构体
int main(int arg, char *args[])
{
FILE *p = fopen(args[1], "w");
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("error is %s\n", strerror(errno));
} else
{
printf("success\n");
struct person man;
memset(&man, 0, sizeof(man));
while(fread(&man, sizeof(struct person), 1, p))
{
printf("id=%d\n", man.id);
printf("name=%s\n", man.name);
printf("age=%d\n", man.age);
printf("tel=%s\n", man.tel);
}
fclose(p);
}
return 0;
}
//写结构体
int main(int arg, char *args[])
{
FILE *p = fopen(args[1], "w");
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("error is %s\n", strerror(errno));
} else
{
printf("success\n");
struct person man[10];
memset(&man, 0, sizeof(man));
man[0].id = 0;
strcpy(man[0].name, "苍井空");
man[0].age = 50;
man[0].sex = 1;
strcpy(man[0].tel, "911");
man[1].id = 1;
strcpy(man[1].name, "饭岛爱");
man[1].age = 20;
man[1].sex = 0;
strcpy(man[1].tel, "119");
fwrite(&man, sizeof(struct person), 2, p);
fclose(p);
}
return 0;
}
//写log的代码
void writelog(const char *log)
{
time_t tDate;
struct tm *eventTime;
time(&tDate);//得到系统当前时间
eventTime = localtime(&tDate);//将time_t数据类型转化为struct tm结构
int iYear = eventTime->tm_year + 1900;
int iMon = eventTime->tm_mon + 1;
int iDay = eventTime->tm_mday;
int iHour = eventTime->tm_hour;
int iMin = eventTime->tm_min;
int iSec = eventTime->tm_sec;
printf("tm_isdst = %d\n", eventTime->tm_isdst);
char sDate[16];
sprintf(sDate, "%04d-%02d-%02d", iYear, iMon, iDay);
char sTime[16];
sprintf(sTime, "%02d:%02d:%02d", iHour, iMin, iSec);
char s[1024];
sprintf(s, "%s %s %s\n", sDate, sTime, log);
FILE *p = fopen("my.log", "a+");
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("write log my.log error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
}else
{
fputs(s, p);
fclose(p);
}
return;
}